Whether we like to pay them or not, we all know that tax revenues are indispensable for our governments to provide good services, such as water and waste services and to build public infrastructure. However, in many countries local governments only receive 10% to 20% of the revenues that could have been collected. This is a resource mobilisation gap up to 80% to 90%. As highlighted by SDG 17, enhancing domestic resource mobilisation, by strengthening the ability of cities and regions to collect revenues, is an important enabler for governments to provide better and more accountable services to their citizens. VNG International advocates the strengthening of local tax administrations and enhancement of revenues from local taxes to finance sustainable service delivery in developing and transitional countries.
Challenges & opportunities
The process of urbanization is an undeniable trend and one of the major challenges for local governments. Over the past decades, urbanization has greatly impacted societies and economies all over the world. By 2030, urban areas are estimated to house 60% of the world’s population. Meanwhile, cities are facing enormous urban challenges including tackling the impact of climate change, insufficient funds to provide basic services, the provisioning of healthcare and education, and to restore deteriorated infrastructure – all of which disproportionately affect the urban poor. Thus, urbanization combined with rapid population growth presents significant obstacles for both the citizens of cities as for their policymakers in particularly lower income and middle income countries.
One of the most pressing of these challenges is the strain put on local public services and infrastructure, namely:
- As urban areas grow, their local governments must accommodate increasing numbers of people while continuing to provide basic services such as water, electricity, and sanitation. This requires significant investment, which can be difficult to secure in a context of limited resources.
- The inadequate infrastructure further strained through urbanization can lead to health and safety hazards, and can hinder economic growth.
- Urbanization can exacerbate social inequalities between rural and urban areas. As cities grow, they often become centres of wealth and power, leading to a concentration of economic and political influence in the hands of a few. This can lead to tensions between different regions and social groups, which results in political instability.
Despite these challenges, urbanization in the developing world presents significant opportunities for growth and development. As cities become centres of economic activity, they can attract investment, generate jobs, and increase productivity. By investing in public services, sustainable urban planning, and infrastructure, cities in the developing world can successfully tackle these challenges while harnessing the opportunities, thereby contributing to a more prosperous and equitable future for their citizens and the overall development of the country.
Own Source Revenue
Reliable and sufficient funding of local governments is crucial for the provision of public services such as water supply, sanitation, and waste management. By investing in public services, cities can create a more liveable and healthy environment for their residents, which can lead to economic benefits such as increased productivity and reduced healthcare costs. For their funding, local governments need a reliable transfer of funds from the central governments (fiscal transfers) as well as a solid own source revenue base.
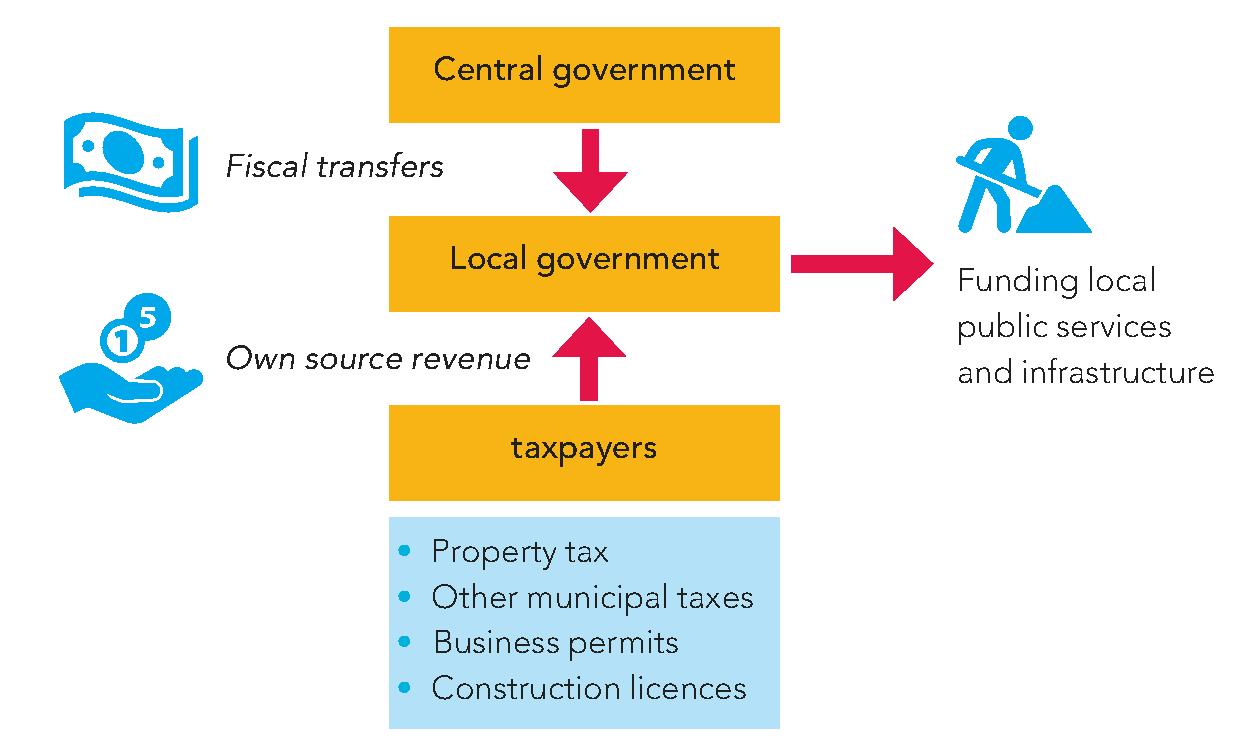
These funds can also be used to:
- Promote sustainable urban planning and development. This includes investments in green spaces, affordable housing, and public transportation systems. A reduction of congestion, air pollution, and other negative environmental impacts associated with urbanization will contribute to the creation of a more liveable and sustainable urban environment. By promoting sustainable urban planning and development, cities can also attract investment, create jobs, and contribute to economic growth, which can help to reduce social inequalities.
- Fund infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation systems. As a result, this will help to improve the access to markets, increase productivity, and reduce transportation costs for businesses and residents.





